AWS X-Ray Investigation
January 15, 2017 #aws #xray #javascript #monitoring
In Zipkin JS Investigation and Zipkin JS Investigation (Part 2), I took a simple Express (Node.js) based web application and added zipkin tracing. I updated that application with support for AWS X-Ray (Preview). The code snippet below was based on instructions found at http://docs.aws.amazon.com/xray-sdk-for-nodejs/latest/reference/.
var express = require('express');
var http = require('http');
var AWSXRay = require('aws-xray-sdk');
var AWS = AWSXRay.captureAWS(require('aws-sdk'));
var app = express();
app.set('port', process.env.PORT || 3000);
app.set('servicename', 'helloservice');
AWSXRay.config([AWSXRay.plugins.ElasticBeanstalk]);
AWSXRay.captureHTTPs(http);
// below not working, need to start with: XRAY_TRACING_NAME=helloservice node index.js
AWSXRay.setDefaultName('helloservice');
app.use(AWSXRay.express.openSegment());
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
// handler code here uses http.request()
});
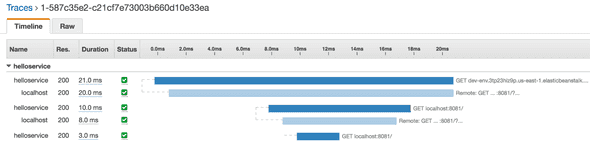
app.use(AWSXRay.express.closeSegment());Looking on the X-Ray Console, here is a screenshot of the result of calling: http://dev-env.3tp23hiz9p.us-east-1.elasticbeanstalk.com/?count=3. I have also included the raw JSON data for this trace.
Amazon uses the X-Amzn-Trace-Id HTTP header with Root and Parent segments for carrying trace ids (see Request Tracing for Your Application Load Balancer for syntax). For example:
X-Amzn-Trace-Id: Root=1-587c35e2-c21cf7e73003b660d10e33ea; Parent=06b7ad9dfdae682a; Sampled=1
To learn more about AWS X-Ray, you can watch AWS re:Invent 2016: NEW LAUNCH! Introduction to AWS X-Ray (DEV316) - YouTube.